CNC Turning: Custom CNC Turning Services in China
High-Precision Turned Components, from Simple Shafts to Complex Multi-Feature Parts.
- ISO 9001 Certified
- Tight Concentricity
- Live Tooling Capabilities
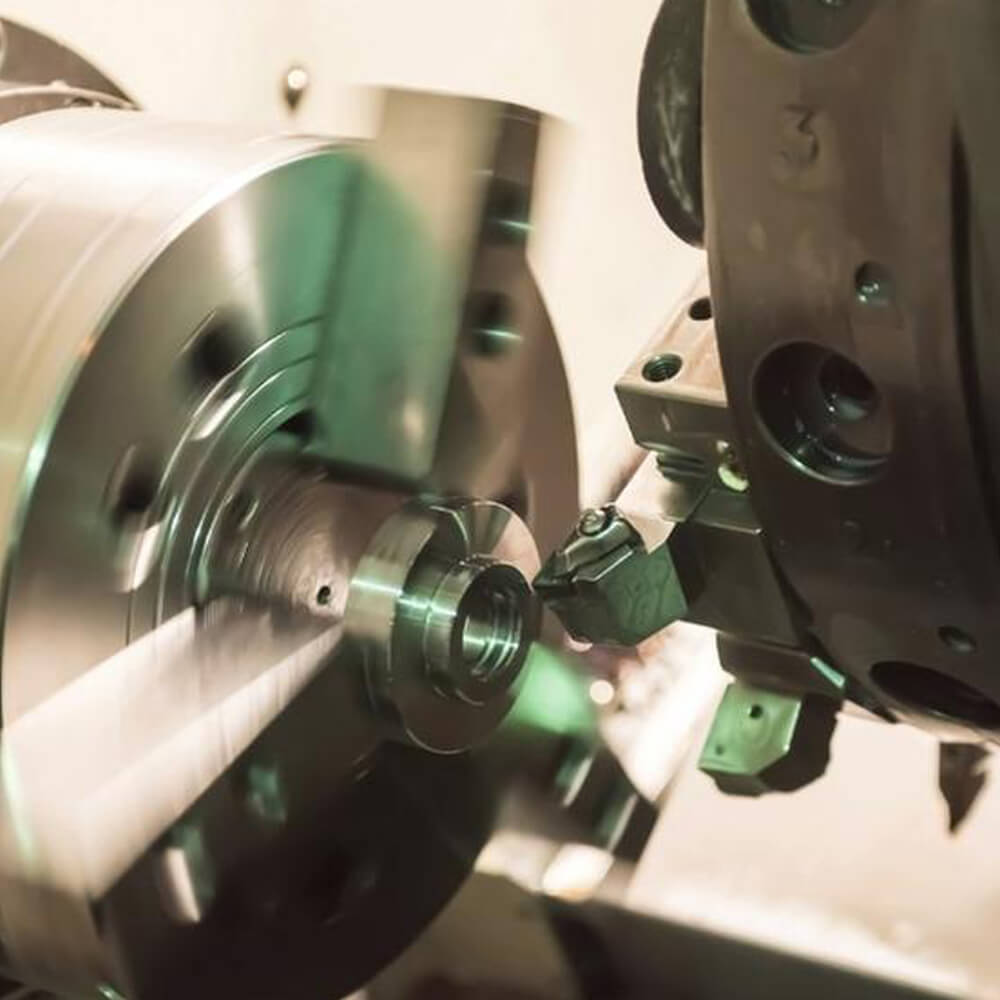
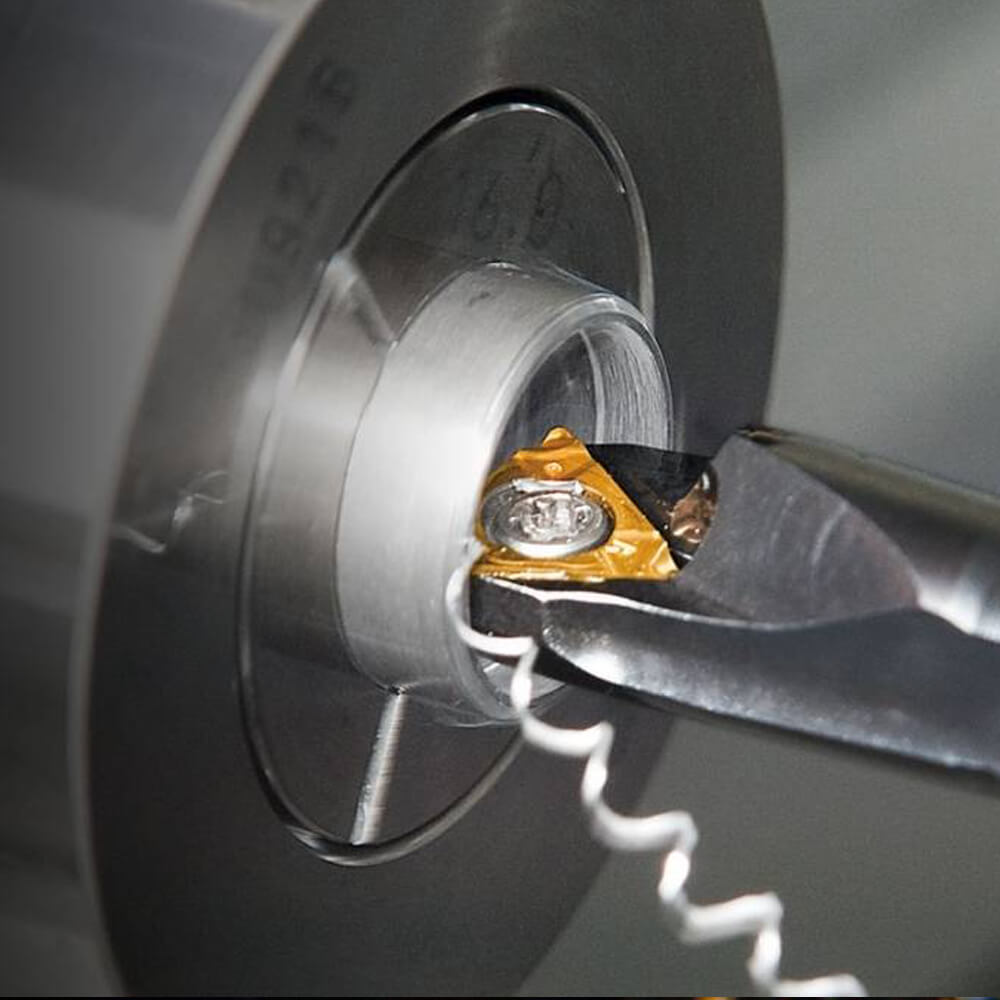


Your Expert Partner for Precision CNC Turning
One of the best companies in China for high-precision CNC turning is Celerity Precision. In this advanced manufacturing process, a cutting tool moves quickly around a workpiece to make complicated cylindrical shapes. We can make parts like shafts, pins, connectors, and fittings with perfect concentricity, tight tolerances, and smooth surfaces thanks to our advanced CNC turning centers. We make perfectly shaped turned parts for any industry, from small prototypes to large production runs.
CNC Turning Materials
Metal
Aluminum is strong, light metal that can be used for many things and doesn’t rust easily.
- Available Grades: 6061, 7075, 5052, 2024, 6063, 6082, 5083
- Common Finishes: As Machined, Anodizing, Powder Coating, Sand Blasting, Chromate (Alodine)

Copper
Copper has great electrical and thermal conductivity, which makes it the best choice for heat sinks and electrical parts.
- Available Grades: C101 (OFHC), C110 (ETP)
- Common Finishes: As Machined, Electropolishing, Plating, Clear Coat

Brass
Brass is great for making fittings and decorative elements since it is easy to work with and looks like gold.
- Available Grades: C360
- Common Finishes: As Machined, Polishing, Plating, Brushing

Bronze
Bronze is durable and has minimal friction, it is widely used for naval hardware, bushings, and bearings.
- Available Grades: C932, C954
- Common Finishes: As Machined, Tumbling

Steel
Steel is a robust, long-lasting, and cheap material that works well in high-stress and industrial settings.
- Available Grades: Mild Steel (1018, 1020), Alloy Steel (4140, 4340), Tool Steel
- Common Finishes: Black Oxide, Zinc Plating, Powder Coating, Painting

Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is very strong and doesn’t rust easily, so it’s great for use in food, medical, and maritime settings.
- Available Grades: 303, 304/304L, 316/316L, 17-4 PH, 416, 420
- Common Finishes: Passivation, Electropolishing, Brushed Finish, As Machined

Magnesium
Magnesium is a very light metal that is great for uses where every gram matters.
- Available Grades: AZ31, AZ91
- Common Finishes: Chromate Conversion Coating

Titanium
Titanium is a high-performance metal that is quite strong for its weight and is also very biocompatible.
- Available Grades: Grade 2, Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V)
- Common Finishes: As Machined, Anodizing (for color), Sand Blasting
Plastic

ABS
ABS is a strong, impact-resistant, and cost-effective thermoplastic that works well for housings, enclosures, and prototypes.
Common Finishes: As Machined, Sand Blasting, Painting

PC (Polycarbonate)
PC is a sturdy, clear material that can handle heat and impact very well.
- Common Finishes: As Machined, Vapor Polishing, Painting

PLA
PLA is a thermoplastic that breaks down naturally and comes from renewable resources. It is often used for quick prototyping.
Common Finishes: As Machined, Painting

PMMA (Acrylic)
PMMA is a clear, hard plastic with great optical clarity. It is widely used as a light-weight substitute to glass.
Common Finishes: As Machined, Vapor Polishing, Flame Polishing

POM (Delrin/Acetal)
POM is an engineering plastic that is low-friction and high-stiffness, making it great for gears and bearings.
Common Finishes: As Machined

PA (Nylon)
PA is a strong and flexible plastic that can stand up to chemicals and wear.
- Available Grades: PA6, PA66
- Common Finishes: As Machined
PE (Polyethylene)
PE is a typical type of plastic that can withstand chemicals and comes in varying densities for different uses.
Common Finishes: As Machined

PEEK
PEEK is a high-performance polymer that is very strong, resistant to chemicals, and stable at high temperatures.
Common Finishes: As Machined

PP (Polypropylene)
PP is a light plastic that is very elastic and resistant to chemicals. It is widely used for living hinges.
Common Finishes: As Machined

HIPS
HIPS is a cheap, stiff plastic that is easy to work with and is typically used to make prototypes before production.
Common Finishes: As Machined, Painting

PBT
PBT is a type of engineering thermoplastic that is stiff, stable in size, and can handle chemicals and heat.
Common Finishes: As Machined

PPA
PPA is a high-performance polyamide that is stronger, stiffer, and more heat-resistant than regular nylon.
Common Finishes: As Machined

PAI (Torlon)
PAI is high-performance plastic that is exceedingly strong and rigid and keeps its qualities even at very high temperatures.
Common Finishes: As Machined

PET
PET is a tough, rigid plastic used in engineering that resists chemicals well and wears well.
Common Finishes: As Machined

PPS
PPS is a high-performance thermoplastic that can withstand chemicals and high temperatures without changing shape.
Common Finishes: As Machined

PS (Polystyrene)
PS is a clear, rigid, and brittle plastic that doesn’t cost much and is typically used for prototypes.
Common Finishes: As Machined, Painting

PVC
PVC is a strong, long-lasting, and cheap plastic that doesn’t easily get damaged by chemicals or water.
Common Finishes: As Machined
PTFE (Teflon™)
PTEE is known for having a very low coefficient of friction, being chemically inert, and being able to handle high temperatures.
Common Finishes: As Machined

Bakelite
Bakelite is a thermoset plastic that is hard, thick, and resistant to heat. It also has good electrical insulating qualities.
Common Finishes: As Machined

FR-4
FR-4 is a glass-reinforced epoxy laminate that is very strong and has great electrical insulation qualities.
Common Finishes: As Machined
CNC Surface Finish Enhance and Protect Your Parts
As Machined
The basic finish, which is the cheapest and most common, has obvious tool marks right from the machine.
Sand Blasting
Makes a smooth, non-reflective matte surface that looks good and helps paint stick better.
Tumbling
A mass-finishing method that quickly removes burrs and smooths off groups of parts.
Electropolishing
Makes metals like stainless steel have a finish that is super smooth, bright, and clean down to the smallest details.
Heat Treatment
A thermal procedure that changes mechanical qualities like strength and hardness (not only for looks).
Alodine
A chemical coating for aluminum that protects it from rust while yet letting electricity flow through it.
Anodizing
Makes a colored surface on metal and titanium that is sturdy, long-lasting, and attractive.
Teflon™ Coating
A fluoropolymer coating that doesn't stick and has low friction. It also resists chemicals very well.
Black Oxide
A conversion coating for steel that gives it a deep black finish without changing its size.
Electroless Plating
A uniform chemical plating procedure (like nickel) that makes all surfaces very hard and resistant to rust.
Electroplating
An electrochemical procedure that puts down a metal layer (such zinc, nickel, or chrome) for decorative or protective purposes.
Painting
A liquid coating that may be sprayed on and comes in a wide range of colors for a decorative and protective finish.
Passivation
A chemical cleaning method that makes stainless steel as resistant to corrosion as possible.
Powder Coating
An electrostatically applied powder dried to provide a finish that is stronger than regular paint.
Electrophoresis
An E-coat procedure that dips items in a coating to cover them completely and evenly.
Brushed Finish
A high-end, refined style with a unidirectional satin grain finish.
Ready to Turn Your Custom Parts?
Why Choose Celerity Precision
Advanced Turning Technology
Our advanced CNC lathes, such as multi-axis centers with live tooling, let us make complicated cylindrical parts with both turned and milled features in one step.
Exceptional Precision and Concentricity
We are experts at keeping tight tolerances on diameters and concentricity, which is very important for high-performance shafts, connectors, and fittings.
High-Volume Production Efficiency
We can run large production orders "lights-out" with automated bar feeders and improved processes. This lowers the cost per part and makes sure that each batch is the same.
One-Stop Manufacturing Solution
We are your full partner, taking care of everything from finding certified materials to precision turning and putting on the final surface finish, all in one place.
Rapid Prototyping Services
Our skilled programmers and machinists can quickly set up and make your custom turned prototypes, which will speed up your testing and development cycles.
Guaranteed Quality Assurance
We check every turned part very carefully to make sure it meets our ISO 9001 standards and your exact needs. We check the dimensions, threads, and surface finish.
From Digital File to Physical Part in 4 Simple Steps
Submit Design & Get Quote
Securely upload your CAD file. Our team provides a detailed quote and DFM feedback within 24 hours.
DFM Review & Order Confirmation
We help optimize your design. Once you approve the quote, we schedule production.
Precision Turning
Your parts are expertly turned on our high-speed CNC lathes by skilled machinists.
Inspection & Global Delivery
Every part is rigorously inspected for dimensional accuracy and concentricity before being securely packaged and shipped to your location.
How We've Helped Our Clients Succeed
Challenge
A client in the automotive industry needed a large number of custom stainless steel sensor housings with complicated internal grooves and external threads.
Solution & Result
We used our CNC lathes with automated bar feeders to run the parts lights-out. This saved us 20% on costs and got us 20,000 perfectly consistent parts on time.
Challenge
A communications company needed a set of brass RF connectors with very tight concentricity tolerances (±0.005mm) to make sure the signal was as clear as possible.
Solution & Result
Using our Swiss-style lathes with high precision, we were able to keep the important concentricity and give the parts a better surface finish, which greatly improved the performance of the client's product.
Challenge
A company that makes machinery needed a complicated drive shaft made of 4140 alloy steel. It needed both turning and milled features, like keyways and flats.
Solution & Result
We made the part in one setup on our multi-axis turning center with live tooling. This "done-in-one" method made sure that the features lined up perfectly and cut the lead time by 40% compared to using separate machines.
Custom CNC Turning Services - Celerity Precision

“The future belongs to those who believe in the beauty of their dreams.” Manufacturers are motivated to strive for accuracy and quality by Eleanor Roosevelt’s remarks. CNC turning services in China are a great option for anyone searching for superior custom parts.
A variety of custom CNC turning alternatives are offered by Chinese companies such as Celerity Precision. They provide prompt service, deal with a variety of materials, and maintain strict tolerances. As a result, China is becoming a major location for CNC turning services, catering to numerous industries globally.
Businesses may swiftly meet their manufacturing needs by utilizing China’s highly qualified workforce and cutting-edge technologies. It is clear from delving into the realm of China CNC turning that this technology has transformed the production of unique parts.
Key Takeaways
- One of the top suppliers of bespoke CNC turning services is China.
- Advanced CNC turning capabilities are provided by businesses such as Celerity Precision.
- Tight tolerances and a variety of materials are supported by custom CNC turning in China.
- One major benefit of CNC turning services in China is their quick lead times.
- China’s CNC turning sector serves a wide range of global sectors.
Introduction to CNC Turning
A lathe is used in the CNC turning process to remove material from a workpiece. The workpiece is rotated around a fixed axis by this machine. It is essential for producing precise custom parts.
What is CNC Turning
One technique that makes use of computer-controlled machinery is CNC turning. It takes material—which could be plastic, wood, or metal—out of a workpiece. A cutting tool glides along the workpiece while it spins, shaping the portion.
This procedure is extremely accurate. It is capable of creating intricately shaped pieces.
How CNC Turning Differs from CNC Milling and Other Processes
CNC milling is not the same as CNC turning. The cutting tool spins and travels during milling in order to remove material. However, during turning, the cutting tool remains stationary while the workpiece rotates along its length.
This distinction alters the parts that can be produced and the process’s efficiency. Important distinctions include:
- Workpiece rotation in relation to cutting tool rotation
- Part symmetry: turning works best for symmetrical or cylindrical pieces.
- Part complexity: more intricate geometries can be produced by milling.
Uses and Benefits of CNC Turning
Numerous industries, including the automotive, aerospace, and medical sectors, use CNC turning. It has the following advantages:
- High levels of accuracy and precision in the fabrication of parts
- Effectiveness in creating symmetrical or cylindrical components
- The capacity to deal with a range of materials, such as composites, metals, and polymers
- Automation-driven labor cost reduction
CNC turning has many applications. It is capable of producing intricately designed components as well as basic parts like shafts and bushings. It is essential in today’s industry because of its accuracy and effectiveness.
CNC Turning Machine Anatomy and Components

Every component of CNC turning machines is essential to the production of parts. Knowledge of these components enhances the machine’s functionality and the caliber of its output.
The Fundamental Design of a CNC Lathe or Turning Machine
The bed of a CNC lathe or turning machine is sturdy. The machine’s components are supported by this bed. It keeps the machine steady and lessens vibrations for increased accuracy.
Key Parts: Headstock, Tailstock, Chuck, Tool Turret, Bed, Control Panel etc.
The main spindle, which rotates the workpiece, is held in place by the headstock. Longer workpieces are supported by the tailstock. The workpiece is securely held by the chuck. Many tasks can be completed without the need for personal assistance thanks to the tool turret, which holds and replaces the cutting tools. The operator can program and operate the machine through the control panel.
The feed system moves the cutting tools, while the drive system powers the spindle. Together, these components enable accurate and effective machining.
Types of CNC Turning Machines (Lathe vs Turning Center; Vertical vs Horizontal)
The types and functions of CNC turning machines differ. A CNC turning center contains additional functionality, such as live tooling, whereas a CNC lathe is only used for basic turning. Large, heavy items are handled using vertical turning machines. General turning is done with horizontal turning machines.
The key to selecting the best machine for your needs is understanding how different machines differ from one another.
CNC Turning Tooling and Materials
Because it can use sophisticated equipment and a variety of materials, CNC turning is a versatile process. We’ll examine typical materials, cutting tools, and the effects of tool wear.
Materials for the Workpiece Frequently Used
CNC turning is capable of working with composites, metals, and polymers. Because of their strength, metals like titanium, steel, and aluminum are often used.
Aluminum is corrosion-resistant and lightweight. Titanium is lightweight, robust, and resistant to corrosion, while steel is strong.
Cutting Tools: Inserts, Tool Holders, Live Tooling etc.
In CNC turning, cutting tools are essential. Tool holders accept cutting tool inserts, which are interchangeable tips. For a range of materials and situations, they are available in a variety of forms and coatings.
The inserts are held in place by tool holders. For precise cuts, their hardness and accuracy are crucial.
CNC lathes can use driven tools for drilling and milling thanks to live tooling. It increases the machine’s adaptability and enables more operations without the need for additional equipment.
Considerations for Tool Wear, Coatings, and Tool Life
A component of CNC turning, tool wear is influenced by material, feed rate, and speed. Tool coatings prolong the life of tools by lowering wear and friction.
Wear resistance, material, and machining conditions all affect tool life. Monitoring and maintaining tools is essential to preventing malfunctions and guaranteeing quality.
| Factor | Influence on Tool Life | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Speed | Higher speeds reduce tool life | Optimize speed based on material |
| Feed Rate | Higher feed rates can increase tool wear | Adjust feed rate for balance between productivity and tool life |
| Tool Coating | Coatings can extend tool life | Choose appropriate coating for the material being machined |
| Material Hardness | Harder materials reduce tool life | Select tools designed for hard materials |
CNC Turning Operations and Techniques

Knowing about the various processes and methods is essential to maximizing the benefits of CNC turning. We can create intricate forms and exact sizes with CNC turning.
Facing
A fundamental phase in CNC turning is facing. It flattens a workpiece’s end. For a smooth finish and the proper length, this is crucial. Facing is used to determine the workpiece’s final length or to prepare it for subsequent procedures.
External Turning
External turning is the process of removing material from a workpiece’s exterior. It can form tapered or straight shapes. On a CNC lathe, this is a typical task.
Boring and Internal Turning
Internal turning and boring are done on the inside of a workpiece. While internal twisting produces intricate structures inside, boring enlarges holes. For the greatest outcomes, these processes require the appropriate equipment and supervision.
Drilling from the Lathe Tailstock / Using Live Tooling
On a CNC lathe, drilling can be carried out using live tooling or the tailstock. The workpiece is held stable while drilling by the tailstock. With live tooling, we may drill and perform other operations without having to move the workpiece, increasing the machine’s speed and versatility.
These turning processes have several key benefits, such as:
- Accuracy and Precision: CNC turning provides accurate control, ensuring that parts fulfill precise specifications.
- Versatility: The CNC lathe is excellent for complex items since it can perform a wide range of operations.
- Efficiency: In CNC turning, doing several stages at once reduces time and increases output.
CNC Turning Process Parameters and Performance Considerations
Process parameters must be carefully considered if you want the best CNC turning output. These consist of depth of cut, feeds, speeds, and other factors. Every element has a significant impact on the operation’s performance.
Speeds, Feeds, Depth of Cut
In CNC turning, feeds, speeds, and depth of cut are crucial. Speed, expressed in RPM, is the workpiece’s rotational speed. In IPR or MPR, feed is the rate at which the tool travels along the workpiece. The amount of material removed all at once is known as the depth of cut.
- A nice finish and long tool life depend on selecting the appropriate speeds and feeds.
- The proper depth of cut minimizes tool wear and aids in effective material removal.
- Productivity can be increased and cycle times reduced by optimizing these.
Surface Finish and Tolerances
In CNC turning, achieving the proper tolerances and surface polish is essential. Material, cutting circumstances, and tool geometry all affect the finish. The permitted variance in part dimensions is known as a tolerance.
Follow these steps to obtain the finish and tolerances you require:
Make use of the appropriate inserts and cutting tools.
For optimal results, adjust the depth of cut, feed, and speed.
Make sure the CNC machine is frequently inspected and serviced.
Chip Formation & Removal, Cooling / Lubrication
A clean and effective machining area is maintained by effective chip creation and removal. Tool wear is decreased, damage is avoided, and finish is enhanced with proper cooling and lubrication.
Think about these points:
- Select the appropriate lubricant or coolant for the material.
- To prevent chip recutting, use efficient chip removal technologies.
- Maintain the CNC machine’s cooling system and check the coolant’s condition.
Machine Rigidity, Vibration & Stability
Accurate outcomes depend on the CNC machine’s stability and rigidity as well as vibration control. By minimizing deflection and vibration, a robust machine arrangement helps the tool stay on course.
- Maintaining the machine’s alignment and proper maintenance will increase its rigidity and stability.
- Make use of sturdy workholding and fixturing tools.
- Optimize toolholder design and minimize overhang.
Manufacturers can enhance CNC turning operations by concentrating on certain process characteristics and performance aspects. Better parts, cheaper prices, and increased efficiency are the results of this.
CNC Turning Design for Manufacturability (DFM) and Limitations

The main goal of CNC turning is to produce parts quickly and affordably. It is quite helpful to know what CNC turning can and cannot achieve. With this information, manufacturers may create parts that are more affordable and simpler to produce while also increasing quality.
Geometric Constraints: Overhangs, Thin Walls, Deep Bores
When it comes to part design, CNC turning has certain limitations. Overhangs require additional support or specialized equipment. During machining, thin walls may vibrate or bend, leading to mistakes or damage. Because deep bores require long, flexible, or vibrating instruments, they are challenging.
Designers can alter their designs to address these issues. They can alter the part’s form or add supports. To make it easier to build, they can also select the appropriate finishes and tolerances.
Turning’s Limitations (What Turning Can’t Do Easily)
CNC turning works well for a lot of things, but not all of them. Complex shapes or sections with lots of little details are not a suitable fit for it. You may need to grind or mill these instead.
Additionally, particularly small or intricate pieces are not the ideal candidates for CNC turning. There may be issues with vibration or precision, and the tools may not fit well.
Cost Factors: Setup Cost, Cycle Time, Material Efficiency
A number of factors affect CNC turning costs. The most important factors are setup cost, cycle time, and material efficiency. Money can be saved by designing components that are simple to assemble and need few tool changes. Time and money can be saved by simplifying the part and requiring fewer steps.
Another important consideration is material efficiency. It has an impact on the amount of waste generated during production. Reducing waste and saving money can be achieved by designing parts with less material.
To put it briefly, designing parts for CNC turning is essential to improving and lowering costs. Manufacturers and designers can improve the production process by considering design constraints and expenses.
CNC Turning Software, Programming and Automation
Proficiency in software, programming, and automation is essential for CNC turning. Makers employ programming techniques and CAD/CAM technologies to achieve high precision and efficiency.
CAD/CAM Turning Tools
In CNC turning, CAD/CAM software is essential. It seamlessly connects manufacturing and design. It enables manufacturers to produce intricate shapes and G-code for CNC machines.
- CAD software is used for component or part design.
- G-code and toolpaths are created for machining by CAM software.
- Better machining is made possible by simulation in top CAD/CAM systems.
Control Systems & G-code Fundamentals
G-code provides instructions to CNC machines. Good CNC turning requires an understanding of G-code and CNC control technologies.
The machine is guided by the control system, which reads G-code. Cool characteristics of contemporary CNC systems include;
- Conversational programming for easier part creation.
- Simulation using graphics to verify the machining.
- Sophisticated diagnostics to address issues.
Automation, Multi-Axis / Live Tooling Enhancements
The productivity and versatility of CNC turning are increased by automation and multi-axis capabilities like live tooling. Live tooling reduces the number of unnecessary stages by enabling drilling and milling on the lathe.
Complex pieces can be produced simultaneously by multi-axis CNC turning centers. This reduces cycle times and increases accuracy. Even greater efficiency is achieved by automation, such as in-process checks and robotic loading.
Manufacturers may achieve unprecedented CNC turning capabilities with the help of these sophisticated software, programming, and automation tools. They get more flexibility, productivity, and accuracy.
CNC Turning Quality, Inspection and Safety

For optimal outcomes, CNC turning requires a strong emphasis on quality and safety. Ensuring the safety of the workplace and the high quality of the parts are crucial.
Methods of Inspection and Dimensional Control
In CNC turning, inspection is essential to determining whether the pieces fulfill the requirements. Various techniques are employed, including:
- Workpiece dimensions can be precisely measured by Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM).
- Optical comparators are used to verify the dimensions and profile of turned pieces.
- Manual Inspection: To confirm measurements and tolerances, operators employ instruments such as calipers and micrometers.
Verifying the workpiece against the design specifications and tolerances is a hallmark of good dimensional control. This ensures that the components are manufactured within the appropriate parameters.
Measurements of Surface Finish and Tolerances Confirmation
A CNC-turned part’s surface finish is crucial. It has an impact on the components’ functionality. Measurements of surface finish are made using:
- Surface Roughness Testers: These instruments evaluate the workpiece’s surface roughness.
- Profilometers: Provide comprehensive information on the topography of the surface.
Verifying tolerances entails confirming that the parts’ measurements fall within the predetermined ranges. For parts to fit and function properly, this is essential.
Guidelines for Safety in CNC Turning
When it comes to CNC turning, safety comes first. Crucial precautions consist of:
- Using guards to prevent unintentional contact with moving parts is known as machine guarding.
- Correct Tool Handling: To prevent accidents, make sure tools are handled and stored securely.
- Providing operators with comprehensive instruction on how to operate CNC turning machines safely.
Manufacturers may produce high-quality parts and maintain workplace safety by concentrating on quality, inspection, and safety.
Applications of CNC-Turned Parts
For many sectors, CNC turning is essential to producing precise parts. It is employed in the production of connectors, shafts, and bushings. This is due to the great precision and accuracy that CNC turning provides.
Industry-specific Examples
CNC turning is required in the automotive industry for components like shafts and bushings. These components must be robust and accurate. For this, CNC turning is ideal.
CNC turning is used in aerospace to create intricate fittings and connectors. These components have to adhere to strict safety and quality requirements. Because it can deal with a variety of materials, including titanium and stainless steel, CNC turning is fantastic.
CNC turning is widely used in the medical industry, mostly for surgical equipment and implants. In this sector, accuracy and the creation of intricate shapes are crucial.
Examples of Performance
Numerous challenging issues, such as working with Inconel and titanium alloys, have been resolved using CNC turning. Complex pieces can now be precisely created thanks to new tools and improved process parameters.
Strong steel, for instance, is used to make high-performance car shafts. Manufacturers can get more precise dimensions and superior surface finishes by refining the CNC turning process.
CNC turning is used in aerospace to create lightweight parts from cutting-edge materials. This lowers weight and increases fuel economy.
Prospective Developments and Trends in CNC Turning
A significant shift is about to occur in the CNC turning sector. New technology and changing production demands are to blame for this. The world of CNC turning is about to alter due to a number of new trends.
Live Tooling, Multi-Spindle, and Swiss-Type Lathes
The use of live tooling is growing in popularity. It enables lathes to drill and mill without the need for additional equipment. This improves accuracy and efficiency.
The number of multi-spindle machines is also increasing. They can work on multiple pieces simultaneously. This increases output and is ideal for producing large quantities of parts.
Additionally, Swiss-type lathes are becoming more popular. They can work with intricate shapes and are renowned for their accuracy. They are ideal for creating intricate, tiny parts.
Automation, Smart CNC, and IoT Integration
By enabling continuous operation and reducing labor costs, automation is revolutionizing CNC turning. Machines are being equipped with intelligent CNC systems. They provide predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring.
- Enhanced effectiveness of the method
- Decreased downtime
- Improved quality of the product
Additionally, IoT (Internet of Things) technology is growing in popularity. It enables remote data monitoring and analysis. This facilitates better decision-making and process improvement for producers.
New Materials, Advanced Coatings, and Sustainable Practices
CNC turning is improving because to new materials and sophisticated coatings. They enhance surface finishes and prolong the life of instruments. They enable us to work with more durable materials as well.
The key now is to make things more sustainable. Manufacturers are recycling and utilizing energy-efficient equipment. These actions save money and benefit the environment.
In the future, CNC turning will continue to develop. New technology and the demand for increased sustainability and efficiency will be its main drivers. Makers can stay ahead of the curve and seize new opportunities by adhering to these trends.
FAQ & Common Misconceptions

As we examine CNC turning, we encounter frequent queries and misconceptions. These must be resolved in order to comprehend its actual potential and constraints.
Frequently Asked Questions
CNC turning is a multifaceted and intricate process. Here are a few important queries and responses:
Which materials can be turned with a CNC machine?
Metals, polymers, and composites are all compatible with it.
With CNC turning, what tolerances are possible?
The machine and material determine tolerances. CNC turning, however, can achieve ±0.001 inches or better.
What makes a turning center different from a lathe?
One axis is used by a lathe to rotate a workpiece. Other tasks performed by a turning center include drilling and milling on several axes.
What does CNC turning mean?
CNC turning is a type of machining. It employs a lathe to take material off of a workpiece. This makes items that are round or cylindrical.
What kinds of things can be employed in CNC turning?
CNC turning can work with a lot of different materials. This comprises metals, polymers, and combinations of the two. Aluminum, brass, stainless steel, and titanium are among examples.
What makes a lathe different from a turning center?
A lathe turns a piece of work around a fixed point. A turning center does more than that. It can spin, mill, and drill, and it generally comes with live tools.
What are the usual tolerances that may be reached with CNC turning?
CNC turning can make very precise parts. These can be as wide as +/- 0.001 inches or as narrow as +/- 0.0001 inches. It depends on the machine and the way it works.
What is live tooling, and how do you use it during CNC turning?
Powered tools are used on a CNC lathe for live tooling. You can drill, mill, or tap without taking the workpiece out of the machine.
What is the difference between CNC turning and CNC milling?
CNC turning turns a workpiece around an axis that doesn’t move. CNC milling moves a cutting tool around a piece of work that is not moving. Turning works well for items that are round or cylindrical.
What are the advantages of making custom parts with CNC turning?
CNC turning is very accurate and works quickly. It can handle complex shapes, therefore it’s perfect for producing custom parts.
Can you automate CNC turning machines?
Yes, it is possible to automate CNC turning machines. This covers systems for loading and unloading robots. It makes things work better and costs less.
When using a CNC turning machine, what safety rules should you follow?
Safety procedures are very important. This includes using the right tools and guarding machines. Also, be careful with the tools and workpieces you use. Teach operators how to avoid mishaps.
What will CNC turning look like in the future?
More live tooling and multi-spindle machines are likely to be popular in the future. There will also be increasing usage of Swiss-type lathes. We will combine automation, smart CNC, and IoT technology. There will also be new materials and ways of doing things that are good for the environment.
Misconceptions
It’s time to set the record straight regarding CNC turning. Here are a few:
- Lathe capacity is only determined by the swing diameter! Swing diameter is important, but other things are too. The distance between the centers, the type of chuck, and the rigidity of the machine are all important.
- CNC turning is only suitable for simple, symmetrical parts! It’s true that it works well for portions that are symmetrical. But current CNC centers can also create complicated, uneven pieces using live tooling and multi-axis technology.
We can fully exploit CNC turning if we know the realities and dispel the myths. In this method, we create parts of great quality quickly.
Final Thought
CNC turning is very important for creating custom parts since it is very accurate and quick. This article has explained how CNC turning uses a number of different tools and methods. These make it possible to make very accurate, complex parts.
It’s vital in a lot of fields, such as aerospace and automobile. CNC turning is useful for making important parts. Custom CNC turning services make products better, speed up manufacturing, and provide you more options.
To sum up, CNC turning is an important part of making things nowadays. It has the accuracy, speed, and flexibility that are necessary in today’s environment, which changes quickly. As we learn more about CNC turning, we’ll find new and interesting ways to use it and make it better.
CNC Turning Resources
CNC Turning FAQ
What is the main difference between CNC turning and milling?
In turning, the workpiece rotates while a stationary tool removes material, which is perfect for creating cylindrical parts. In milling, a rotating tool removes material from a stationary workpiece, which is better for creating prismatic shapes, pockets, and holes.
What is "live tooling" on a CNC lathe?
Live tooling refers to powered, rotating cutting tools (like end mills and drills) mounted in the lathe’s turret. This allows us to perform secondary milling, drilling, and tapping operations on the part without moving it to a separate milling machine.
What is the maximum diameter and length you can turn?
Our turning capabilities can accommodate parts with diameters up to [Insert Max Diameter, e.g., 400mm] and lengths up to [Insert Max Length, e.g., 1000mm]. Please contact us for specific inquiries.
What is Swiss-style turning?
Swiss turning is a specialized type of CNC turning where the workpiece is fed through a guide bushing. It is ideal for producing very small, long, and slender parts with extremely high precision.
What kind of tolerances can you achieve with CNC turning?
We can consistently achieve diametrical tolerances of ±0.01mm (±0.0004″). For critical features, even tighter tolerances are possible depending on the material and part geometry.
What is a bar feeder, and what is its advantage?
A bar feeder is an automated system that continuously feeds long bars of material into the CNC lathe. This allows for uninterrupted, “lights-out” production of thousands of parts, which significantly reduces the cost per part for high-volume orders.




