Custom Die Casting Services in China
Rapid, High-Volume Production of Complex Metal Parts with Excellent Surface Finish.
- ISO 9001 Certified
- Aluminum & Zinc Alloys
- In-House Tooling & CNC Machining
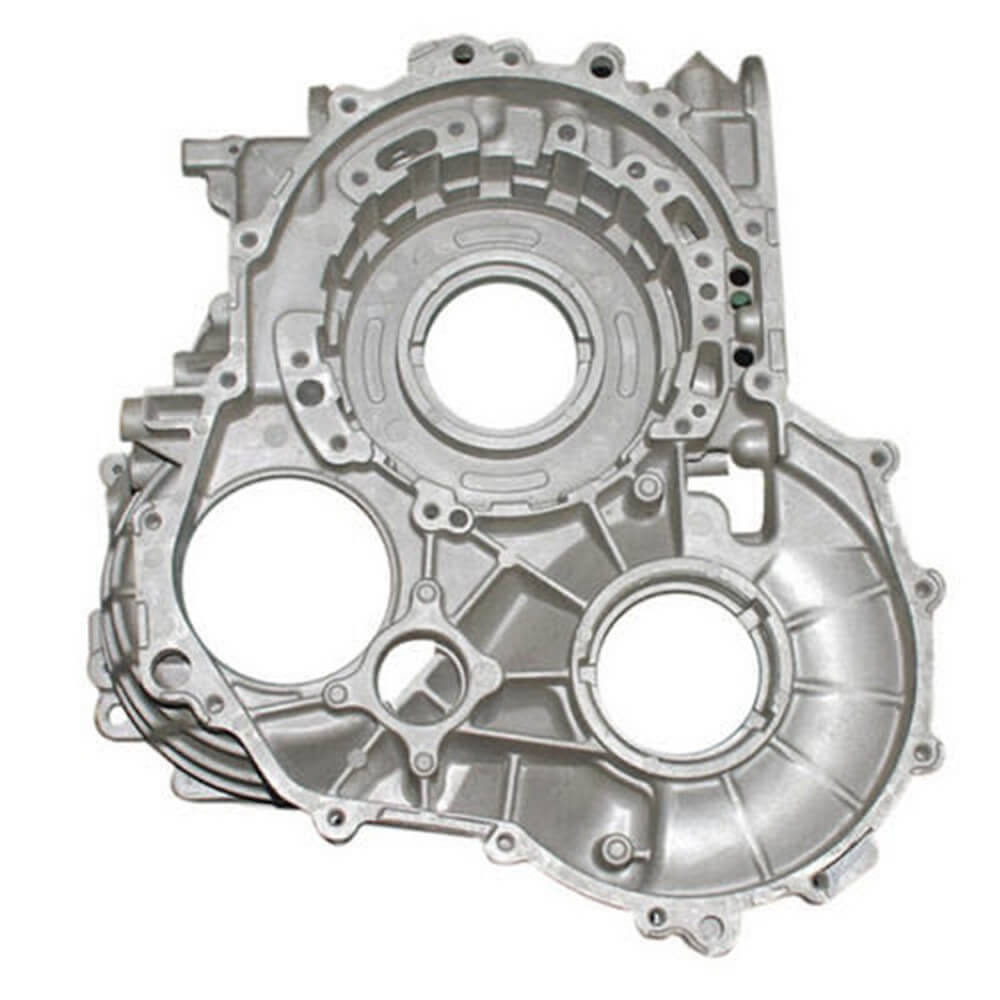

Your Expert Partner for Die Casting Manufacturing
Celerity Precision offers comprehensive high-pressure die casting services in China, providing a highly efficient solution for manufacturing complex metal parts in medium to high volumes. Die casting is a process where molten metal is forced into a hardened steel mold (a die) under high pressure. This method is ideal for producing parts with intricate details, thin walls, and excellent dimensional accuracy at a very rapid pace. Our integrated services cover every stage of the process, from expert Design for Manufacturability (DFM) and in-house tool making to high-volume casting, precision secondary machining, and final surface finishing.
A Complete Solution from Tooling to Finished Part
We provide a seamless, end-to-end die casting solution, ensuring quality, efficiency, and accountability at every step of the manufacturing process.
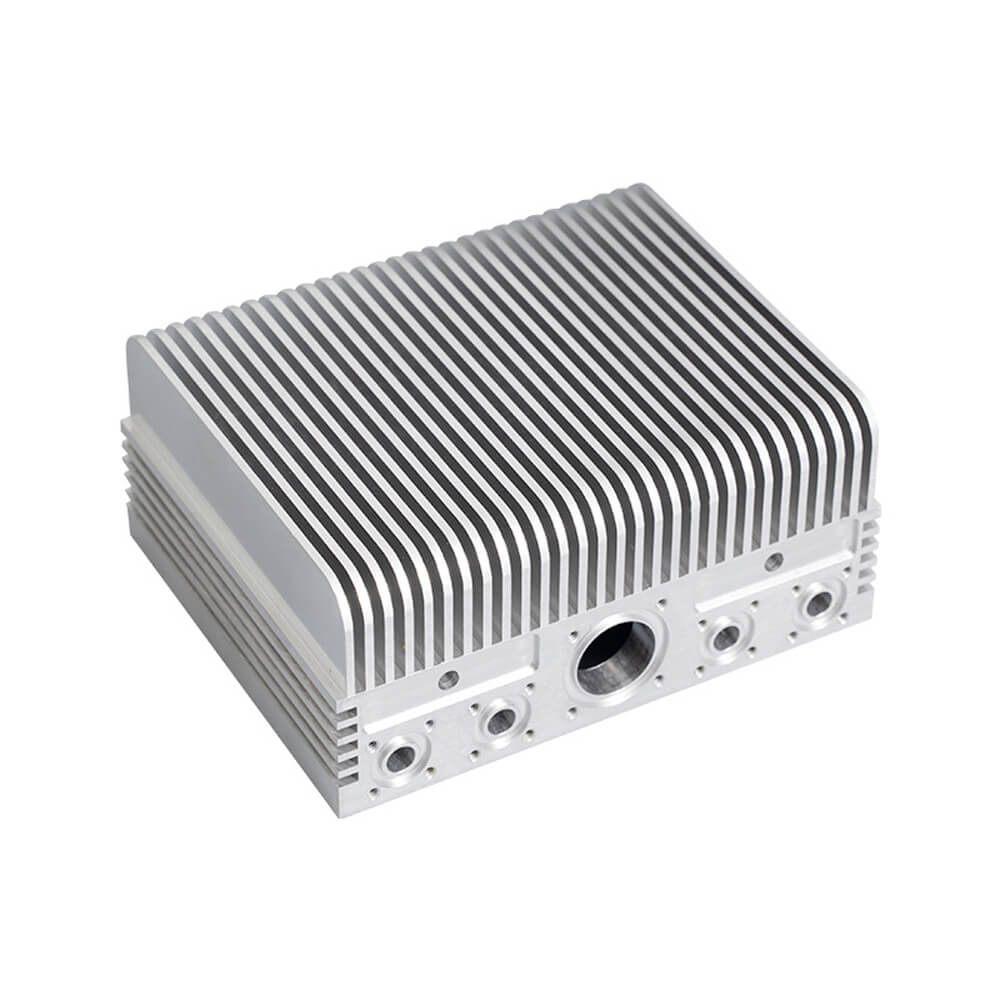

Expert DFM and Mold Flow Analysis
Before any tool is cut, our engineers perform a thorough Design for Manufacturability (DFM) and mold flow analysis. This critical step helps optimize your part design for the casting process, ensuring proper material flow, minimizing porosity, and guaranteeing the long-term success of your project.
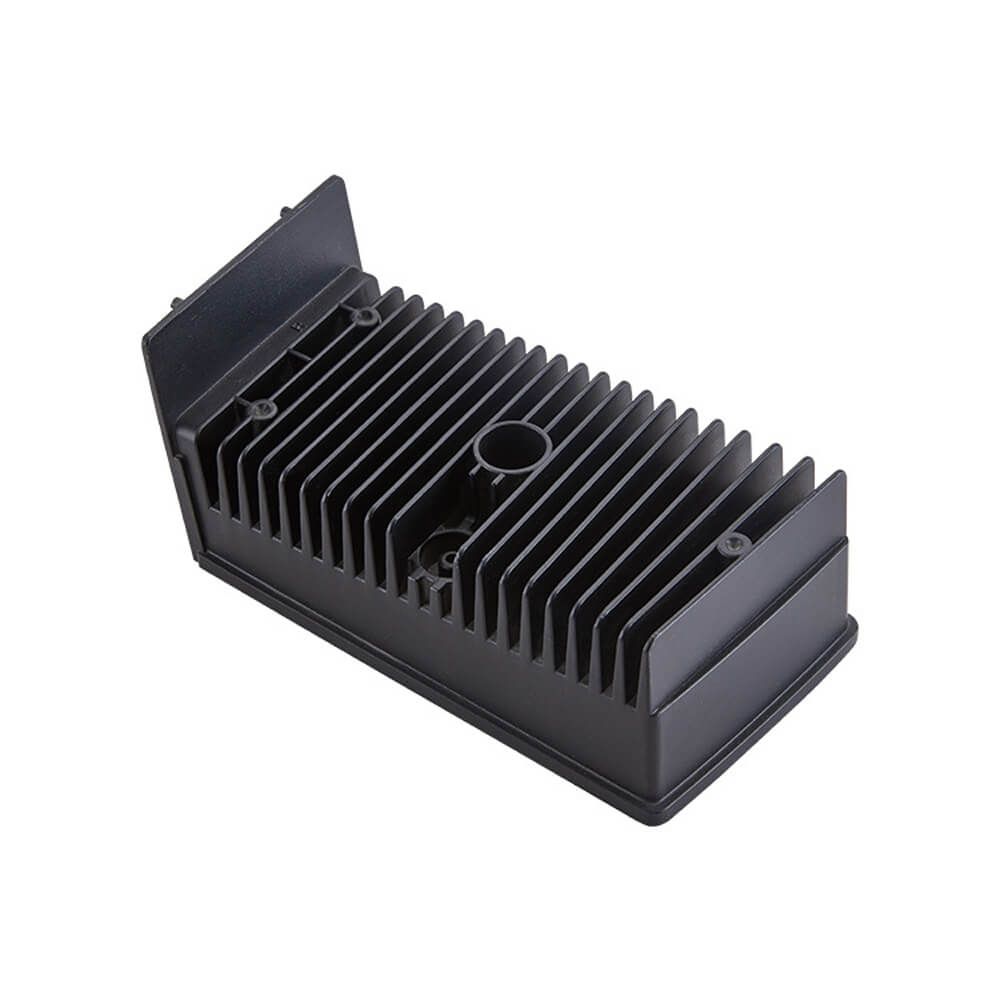

In-House Tool & Die Making
We design and manufacture high-quality, hardened steel dies in-house. By controlling this crucial first step, we can ensure the tooling is built to the highest standards for longevity and precision, reduce lead times, and make rapid modifications or repairs as needed.
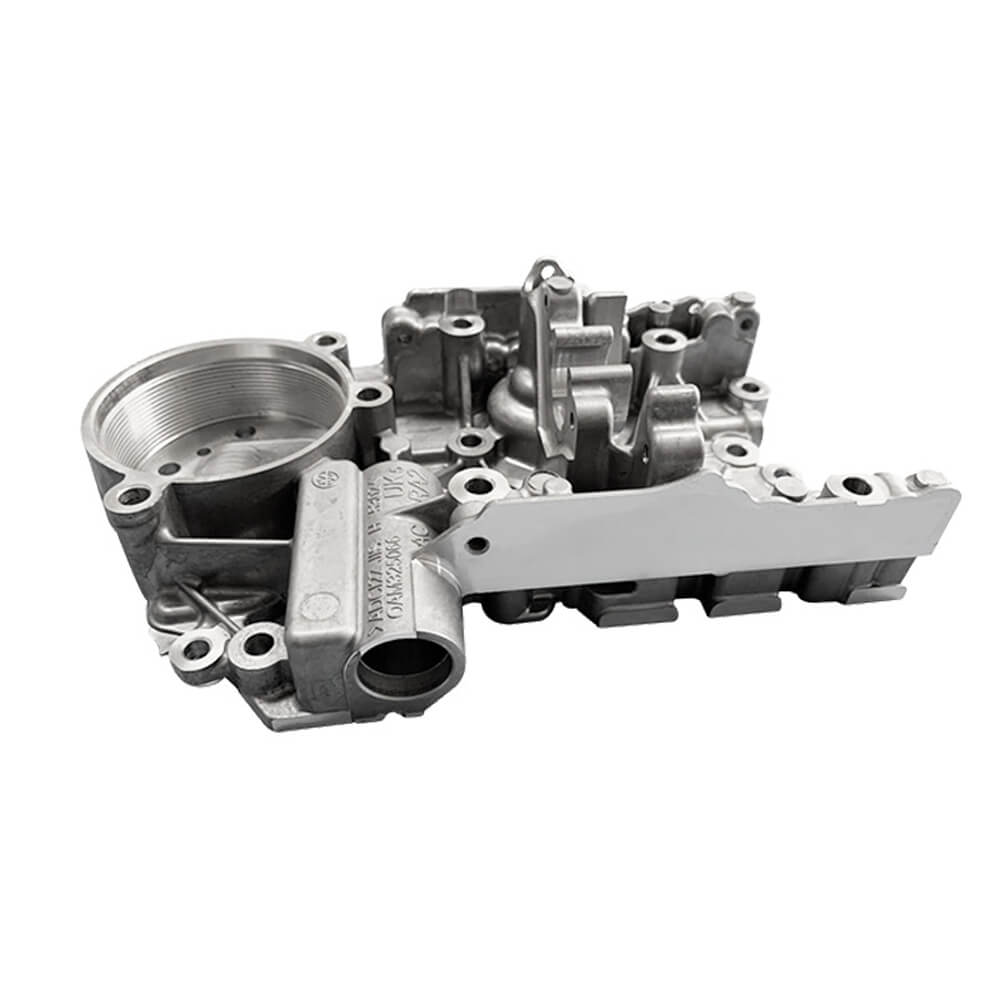

High-Pressure Casting Production
Our factory is equipped with a range of modern, automated hot and cold chamber die casting machines. This allows us to efficiently produce parts from aluminum and zinc alloys, maintaining consistent quality, rapid cycle times, and cost-effectiveness for production runs from a few thousand to hundreds of thousands of parts.
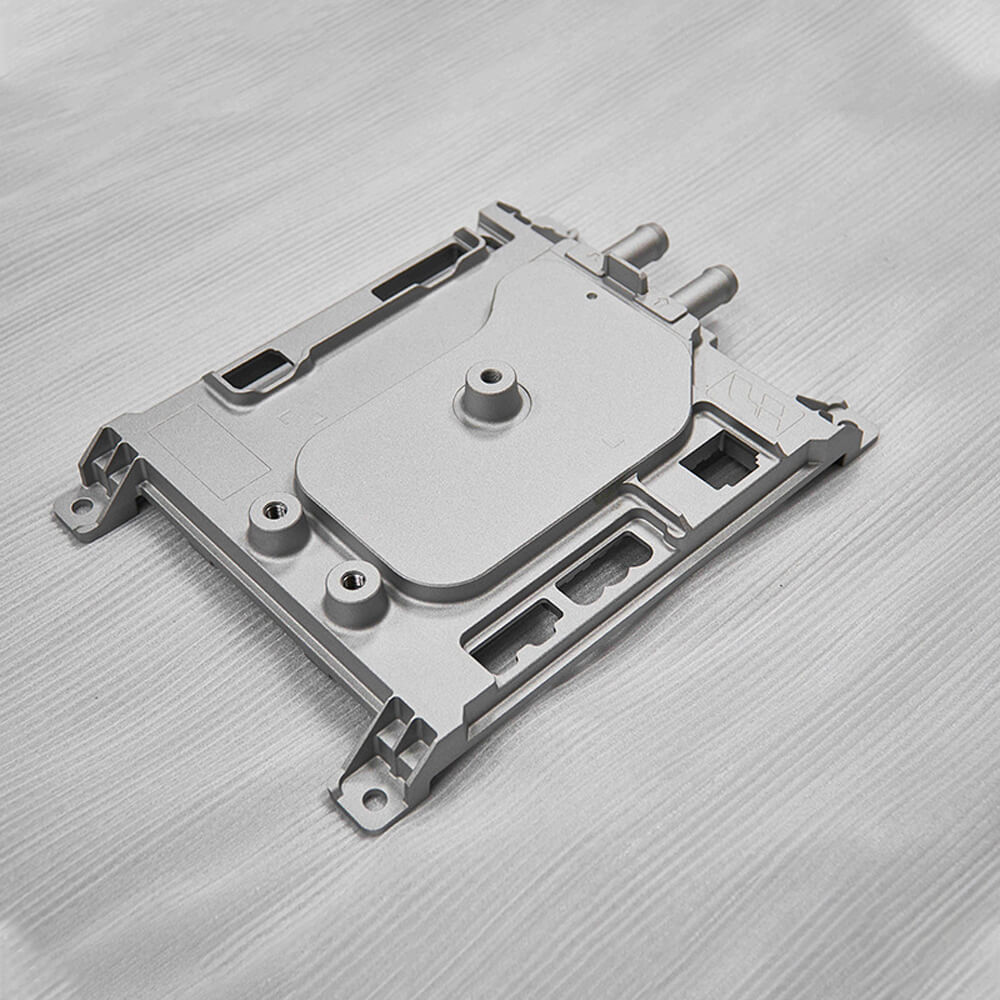
Precision Secondary CNC Machining
Raw die-cast parts often require secondary machining to create features that cannot be cast-in, such as tapped holes, precision bores, or mating surfaces with very tight tolerances. Our in-house CNC machining department is fully equipped to perform these critical operations, transforming your near-net-shape casting into a final, precision component.
High-Performance Casting Alloys
Metal
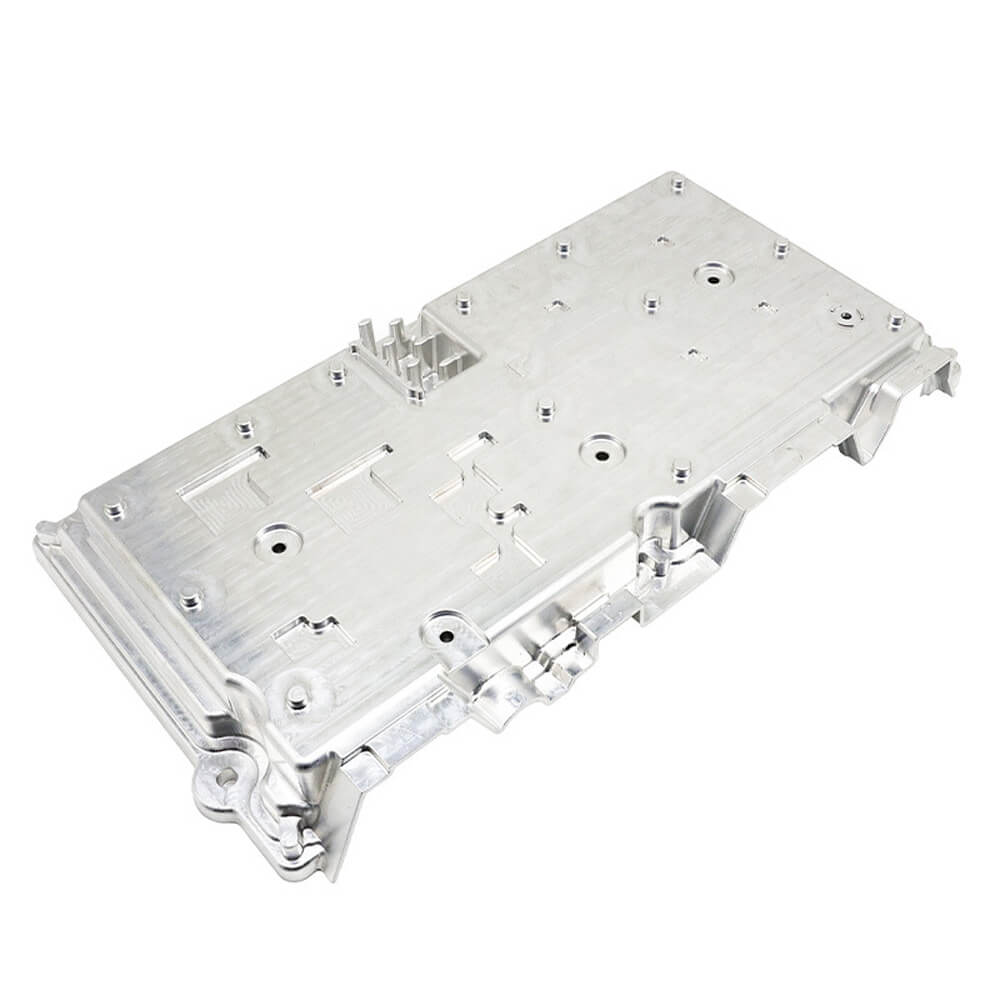

Aluminum Alloys
- A380 (ADC12): The most popular die casting alloy, offering an excellent combination of castability, mechanical properties, and thermal conductivity. Ideal for a wide range of applications from electronic housings to automotive components.
- AlSi12: Known for its excellent fluidity and pressure tightness, making it a great choice for intricate and leak-proof castings.

Zinc Alloys
- Zamak 3: The most common zinc alloy, it is easy to cast, provides a superior surface finish, and is ideal for subsequent plating.
- Zamak 5: Offers higher strength and hardness than Zamak 3, making it a good choice for parts requiring greater structural integrity.
Have a Design Ready? Let's Make It Real.
Why Choose Us for Die Casting
Integrated One-Stop Solution
We manage the entire process under one roof: from DFM and tool making to casting, CNC machining, and final finishing. This eliminates complex supply chains and ensures total accountability.
Expert Engineering and Tooling Design
Our deep expertise in tool design and mold flow analysis ensures your parts are optimized for high-volume production, resulting in higher quality and lower costs over the life of the project.
Rapid Tooling and Production Startup
Our in-house tool making capability allows us to produce your custom die casting mold and start production faster than companies that outsource this critical step.
Precision Where It Counts
We combine the speed of die casting with the precision of CNC machining. We cast the near-net shape quickly and then machine the critical features to the tight tolerances you require.
Consistency for High-Volume Production
Our automated die casting and CNC processes deliver exceptional part-to-part repeatability, ensuring that the thousandth part is identical to the first.
Complete Finishing and Assembly
After casting and machining, we can provide a full range of finishing services, including powder coating, painting, and plating, to deliver a product that is ready for your assembly line.
Advantages of the Die Casting Process
Excellent for Mass Production
Die casting has an extremely fast cycle time, making it one of the most cost-effective methods for producing metal parts in high volumes.
Complex Geometries and Thin Walls
The high-pressure process allows for the creation of intricate, complex net-shape parts with very thin walls, which is difficult with other methods.
Superior Dimensional Accuracy and Stability
Die-cast parts are dimensionally stable and hold their tolerances very well, ensuring excellent part-to-part consistency.
Excellent Surface Finish
Produces a very smooth surface finish as-cast, which can be further improved with minimal secondary preparation for cosmetic finishes.
Integrated Features
Features like bosses, studs, and threads can often be cast directly into the part, reducing the need for secondary assembly operations.
High Strength and Rigidity
Die-cast parts offer an excellent combination of stiffness and strength, especially relative to plastic injection molded parts.
From Design to Mass Production in 4 Key Stages
Design, DFM & Tooling
We work with you to optimize your design, then we manufacture the hardened steel die for your project in-house.
First Article Inspection (FAI)
We produce the first batch of parts ("first shots") from the new tool and perform a rigorous inspection to ensure they meet every specification.
High-Volume Casting & Machining
Once the FAI is approved, we begin full-scale production, including any required secondary CNC machining operations.
Finishing, Assembly & Delivery
We apply the specified surface finish, perform any final assembly, and then package and ship your completed parts.
Custom Die Casting Services - Celerity Precision

Are you looking for a means to create metal parts with complicated shapes that are also excellent quality? Many industries use die casting as their first choice.
We pour hot metal into a mold with a lot of pressure. This lets you produce parts that are exactly the right shape and smooth. Because of its advanced technology and skills, China is currently a major center for die casting.
There are many die casting services available in China. This involves die casting with zinc and aluminum. We’ll take a look at die casting in this article. We’ll talk about the different kinds, materials, techniques, and purposes of it.
Important Points
- Die casting is a way to make metal items that are very good.
- Die casting is done really well in China.
- In China, there are several places that offer custom die casting services.
- Die casting often uses aluminum and zinc.
- Die casting is utilized in many different fields.
Introduction
People have been die casting for more than 100 years. It has become an important way to produce metal pieces with a lot of detail. Many businesses utilize it to make complicated parts.
What is Die Casting? A Definition
Die casting is a method of making metal pieces by putting hot metal under a lot of pressure into a die. It’s perfect for parts that need to be exact. This approach is utilized for pieces that need to be very precise.
Experts claim that die casting is when hot metal is forced into a mold under a lot of pressure. Then it hardens. This shows how crucial it is to be precise and put pressure on the die.
The Past and Present of Die Casting
In the late 1800s, the first machines for die casting were built. Over the years, the method has gotten a lot better. This is because of new technology and the need for things to work better.
Historians say that die casting has changed a lot over the years. Better machines and new alloys have been helpful. These improvements have made it possible to make parts with shapes that are hard to understand.
Die casting has altered a lot since it first started. It has changed to meet the needs of industries like autos and planes. Today, it makes items with very precise dimensions and smooth surfaces.
Types of Die Casting Processes

There are several ways to do die casting, which makes it a flexible way to make things. Each method works better with various types of materials and pieces. The proper procedure depends on the metal, how complicated the part is, and how good you want the output to be.
Die Casting in a Hot Chamber
Hot-chamber die casting works with metals like magnesium and zinc. A machine’s crucible melts the metal. After that, it is squeezed into a die cavity. This approach works quickly and is suitable for parts that are small to medium in size.
Die Casting in a Cold Chamber
Cold-chamber die casting is used for metals like copper and aluminum. A different furnace melts the metal. Then, it is put in a cold chamber and squeezed into the die. This method works for parts of all sizes and levels of difficulty.
Other Types of Die Casting or Specialized Die Casting Methods
There are more specific ways to cast dies. Parts made by vacuum die casting have decreased porosity. Squeeze casting makes the mechanical qualities better. These approaches are tailored to the needs of the industry and improve the quality of the products.
| Die Casting Process | Metals Used | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Hot-Chamber | Zinc, Magnesium | High production efficiency, suitable for small to medium-sized parts |
| Cold-Chamber | Aluminum, Copper | More versatile, suitable for a wide range of part sizes and complexities |
| Vacuum Die Casting | Various | Reduced porosity, improved part quality |
“Choosing the right die casting process is key for quality and cost. Knowing the different methods helps manufacturers make better choices and improve their processes.” Industry Expert
Materials and Alloys
Aluminum, zinc, and magnesium alloys are some of the materials used in die casting. Choosing the proper material is very important. It has an effect on the qualities and quality of the final product.
Alloys That Are Commonly Used
Die casting can be used with a lot of different alloys, each of which has its own unique properties. The most popular ones are:
- Aluminum Alloys: They are light, don’t rust, and transfer heat well. Cars and planes need a lot of aluminum alloys.
- Alloys of Zinc: Zinc alloys can be bent, hold their shape effectively, and be cast thin. They’re fantastic for parts for cars and hardware.
- Magnesium Alloys: When die casting, magnesium is the lightest metal employed. It is robust, easy to cast, and easy to work with. It’s great when you need to lose weight.
Material Characteristics Important for Die Casting
The characteristics of the alloys used in die casting are particularly essential. They have an effect on the way the casting is done and the features of the finished product. Some important features are:
- Melting Point: The temperature at which the alloy becomes liquid. It changes the amount of energy needed and the tools employed.
- Fluidity: How well the melted alloy fills the space in the die. It affects how detailed and complicated the part is.
- The alloy’s mechanical qualities include strength and durability. They tell you how well the part works in different situations.
It’s important to know these things in order to choose the suitable alloy for a job. It makes ensuring that the finished product satisfies the necessary standards and works as expected.
Die Casting Process / Workflow

There are a lot of steps in the die casting process. It needs to be done with care and precision. It starts with designing the mold and finishes with finishing the product.
Mold / Die Design and Tooling
The first step is to make the mold or die and design it. This step is very important since the quality of the mold impacts the quality of the product. When designing a mold, you have to take into account how the material will shrink and where the separating lines will be. The mold is composed of high-quality steel so that it can handle the high heat and pressures of the process.
Injection of Molten Metal, Cooling and Solidification
After that, a die casting machine fills the mold with molten metal. The kind of machine you use depends on the metal you are casting. The metal cools and hardens in the mold once it has been filled. The time it takes to cool down is essential and relies on how thick the casting is and how hot the mold is.
Steps for Ejection and Post-Processing
The mold opens and the casting comes out once it has hardened. After that, the casting goes through post-processing stages. These include trimming, machining, and surface treatments like polishing or coating. These stages are very important for the part’s quality and precision.
To manufacture high-quality components quickly, it’s important to know and improve each step of the die casting process. The procedure is adaptable and may be used for a wide range of tasks, from making small pieces to big, complicated ones.
Die Casting Applications
Die casting is a flexible way to make things that is utilized in many different fields. It can make shapes that are hard to make and surfaces that are smooth. This is why it’s a great choice for producing bits and pieces.
Many businesses use die casting, such as
- Automotive: pieces of the engine, transmission, and other structural pieces.
- Aerospace: Parts that need to be very precise and last a long time.
- Consumer Electronics: Cases, frames, and other elements for electronic devices.
These industries benefit from die casting’s ability to make pieces that are very precise in size and have a smooth surface.
Die casting has been utilized by many businesses to produce complicated parts. It’s utilized for engine blocks and cylinder heads in the car industry. It’s utilized to make smartphone cases in the consumer electronics industry.
Die casting is a good illustration of how aluminum alloy parts for electric vehicles are made. This makes them work better and gives them more range.
These examples show how die casting may be used in many different fields and is quite effective.
Design Considerations and Guidelines
Designers have to follow certain rules in order to manufacture good die castings. These criteria help make sure that the end output is what you anticipate and has no problems.
Thickness of the Wall, Angle of the Draft, and Uniformity
The thickness of the wall is an important part of the design. To avoid problems like porosity and shrinkage, the thickness should be the same all around. People usually say that it should be at least 0.8 mm, but this can differ depending on the alloy. Draft angle is also important since it makes it easier for the casting to come out of the die. Most of the time, a draft angle of 1 to 2 degrees is best.
The designs should also be the same. If the thickness changes, it might cause problems with cooling that lead to flaws. To make sure that cooling and solidification happen correctly, try to make the thickness even.
Parting Line, Fillets, Radii, and Undercuts
The die halves meet at the separation line. It’s vital to plan this region carefully so that there isn’t too much material and the division is clean. Fillets and radii are also important since they help lower stress and make the casting stronger.
Try to avoid undercuts or keep them to a minimum. If you need to, think about employing side actions or slides in the die design to deal with these elements.
Designing to Eliminate Defects
Good design can help eliminate defects including porosity, misruns, and cold closes. To let gases escape during casting and lower porosity, it is important to vent properly. The design should also assist the die cavity fill up smoothly so that there are no cold shuts or misruns.
Controlled solidification is also very crucial. To avoid shrinkage flaws, designers should plan for solidification. You can do this by making sure that the thickest areas are well-fed and designed for progressive thickness fluctuations.
“A well-designed die casting can significantly reduce the need for post-processing and improve the overall efficiency of the manufacturing process.” – Industry Expert
Manufacturers can make high-quality die castings by following these design rules. These castings will be free of flaws and meet all the requirements.
Advantages of Die Casting

Die casting is special because it is both fast and precise. It is known for creating pieces with complicated shapes that are of great quality.
High Speed and Efficiency in Production
Die casting works extremely well. It can create a lot of parts quickly, which is great for big orders. The process is mechanized, which saves money and makes sure that all the pieces are the same.
Good Accuracy in Size and Surface Finish
Parts made by die casting are highly smooth and exact. It fits pieces well and makes them appear beautiful without any further labor. This is important for items that need to fit well or look good.
Ability to make Thin Walls and Complicated Shapes
Die casting can manufacture parts with walls that are thin and shapes that are hard to make. This is perfect for businesses that need parts that are light and detailed. It can make shapes that other technologies couldn’t.
Cost Savings in High-Volume Production
To start die casting, you need to buy a lot of tools. But the more pieces you create, the less it costs. This makes it a good choice for creating a lot of pieces.
Disadvantages and Limitations
There are a lot of good things about die casting, but there are also some bad things. Knowing these limits will help you figure out if die casting is the best option for some tasks.
High Initial Tooling / Die Costs
The high cost of creating the tools and dies is a key challenge with die casting. This might be a huge problem for organizations with restricted costs or for creating tiny batches.
Limitations of the Material
Most of the time, die casting uses metals like aluminum, zinc, and magnesium. This means that it won’t work for pieces that require to be made of iron or other metals.
Porosity, Defects, Surface Imperfections
Die casting often makes parts that have holes or other problems. These can make parts weak or not up to standards for quality. Also, the surface might not look or operate as well as it should.
Part Size, Complexity, or Low Volume Economies Limitations
Die casting can’t handle parts that are too huge or too complicated. Also, the high cost of tools makes it not cost-effective for creating small batches.
In short, die casting has a lot of good points and a few bad ones. Manufacturers can utilize them to figure out when to use die casting and how to deal with its problems.
Factors Affecting Cost

To save money, you need to know what affects the cost of die casting. The price of die casting depends on how much the tools and dies cost, how much the materials cost, and how long it takes to make the part.
Costs of Tools and Dies
Making the die casting tools costs a lot of money up front. The design, size, and die material of the part all matter. More detailed tooling is needed for complex designs, which costs more. Also important are how long the die will last and how many parts it will manufacture.
Choosing an alloy and the cost of materials
The cost of materials is very important in die casting. The type of alloy you choose might have a big impact on the price. People like aluminum and zinc alloys because they are cheap and work well. But the price isn’t just for the alloy. It also relies on how easy it is to recycle and how much waste is made during production.
- People appreciate aluminum alloys because they are strong and light.
- Zinc alloys work well for small, intricate pieces.
- Magnesium alloys are useful for the aerospace industry because they are light and robust.
Cycle Time, Use of Machines, and Post-Processing
The cost of making a part is affected by how long it takes to create it. Making more parts in less time saves money. It’s also necessary to know how to use machines and maintain them working. Quality requires steps like machining or polishing, which raise the price.
- Use innovative technology to speed up cycle times.
- Look for ways to make post-processing less expensive.
- To avoid downtime, keep machines in good shape.
By keeping an eye on these things, manufacturers may lower the cost of die casting while still making sure the quality stays good.
Quality Control and Defects
To develop high-quality die castings, manufacturers must follow tight quality control measures. Die casting needs to have good quality control. It helps lower the number of mistakes and makes sure the end product is good.
Common Problems with Die Casting
Mistakes in die casting might make the end product less useful and of lower quality. Some common problems are:
- Porosity: This happens when gas is trapped or the metal shrinks when it cools.
- Misruns arise when the molten metal doesn’t completely fill the die cavity.
- Cold shuts happen when two streams of molten metal meet but don’t mix properly.
- Shrinkage: This happens when the metal shrinks as it cools down.
To put up good quality control methods, you need to know about these problems.
Standards and Methods for Inspection
There are numerous approaches and standards for checking the quality of die castings. These are:
| Inspection Method | Description | Standards |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Looks at the surface for issues like porosity, misruns, and cold shuts. | ASTM E1251 |
| Radiographic Inspection | Uses X-rays to spot internal flaws like porosity and shrinkage. | ASTM E94 |
| Dimensional Inspection | Checks if the casting fits the exact size needed. | ISO 286 |
By following the correct standards and employing certain inspection procedures, producers may be sure that their die castings are of good quality.
Surface Treatments and Finishing

Die-cast pieces go through a number of finishing stages to acquire the right look and feel. Machining and coating are two of these. These procedures are very important for having the final result appear attractive and work well.
Choices for Finishing
There are many ways to treat die-cast items to make their surfaces better. Here are some common ones:
- Machining: To get the right sizes and flawless finishes.
- Coating: To protect, make something appear better, or both.
- Polishing means making the surface smoother and getting rid of tiny defects.
Experts state, “The right treatment and finish for a surface depend on what the product needs.”
“Surface finishing is not just about aesthetics; it’s also about making die-cast parts last longer and work better.”
How Surface Finish Affects Performance and Looks
How die-cast parts look and work depends a lot on how they are finished. A nice polish can:
- Make them less likely to rust.
- Make them live longer.
- Make them look better.
Picking the correct finishes and surface treatments is very important. It helps make sure that the pieces appear good and operate well. Makers may make sure their die-cast parts are of the highest quality by using the best finishing procedures.
Sustainability, Recycling and Environmental Aspects

As we pay greater attention to the environment, die casting is becoming more eco-friendly. It’s apparent that recycling and saving energy are two important ways to lessen its effect on the earth.
Recyclability of Alloys and Waste Material
Aluminum and zinc are two metals that may be recycled that are used in die casting. You may use these over and over again without losing their quality. This saves resources and reduces waste.
We’re making die casting less wasteful by employing closed-loop recycling. This method is good for the environment and saves money because it uses fewer raw materials.
Energy Consumption, Carbon Footprint and Improvements
It takes a lot of energy to melt metals and run machinery for die casting. But new technology and better ways of doing things have made it use less energy.
We’re trying to decrease our carbon footprint by utilizing less energy and more renewable sources. This will help us make die casting even better for the environment.
- Using melting and holding furnaces that use less energy.
- Making the most use of machines to cut down on idle time.
- Putting money into renewable energy sources to make electricity.
We want to make die casting last longer. This will make it a better option for businesses who want to be green.
Comparisons with Other Casting / Manufacturing Methods

Die casting is different from other casting methods. It has its own pros and cons. Knowing these differences can help you pick the best way to make something.
Casting with Sand, Die, or Investment
There are numerous ways to cast metal, such as die casting, sand casting, and investment casting. Die casting is quick and can manufacture pieces with thin walls and complicated forms. Die casting is more accurate than sand casting, but sand casting can handle bigger and more complicated items. Investment casting is a good way to make pieces with intricate designs and smooth surfaces.
There are a few things to think about while comparing these strategies. These include how much you want to make, the qualities of the material, and how precise you need to be. For instance, die casting costs less for large orders. For small batches or prototypes, sand casting is better. Investment casting is used for pieces that need very precise shapes and patterns.
When Die Casting Is More or Less Useful
Die casting is the greatest way to make a lot of pieces with thin walls and complicated shapes. It’s utilized to make crucial parts for cars and planes. But it’s not the greatest for parts that are very big or very little, or parts that have highly complicated forms on the inside.
To sum up, die casting has both good and bad points. It’s about right for some jobs. Manufacturers can choose the best one for their purposes if they know how it stacks up against other ways.
Final Thoughts
Die casting is still one of the most accurate and efficient ways to make metal. It is a key part of modern industries like automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics because it can make complicated, high-quality, and long-lasting parts. Die casting is always getting better thanks to new materials, automation, and process control. This means that it is even more consistent, performs better, and costs less.
China has become the world’s top provider of custom die casting services thanks to its cutting-edge technology, talented workers, and low prices. Chinese manufacturers offer custom solutions that match worldwide quality standards, from aluminum and zinc alloys to specialist methods like vacuum or squeeze casting.
Die casting’s capacity to be recycled and its ability to use the best materials are important for decreasing environmental effect as businesses progress toward sustainability and energy efficiency. Choosing the proper die casting partner guarantees not just great products but also long-term value and new ideas.
In short, die casting is a reliable, scalable, and long-lasting way for enterprises to get metal parts that are made to exact specifications. Custom die casting services in China have the knowledge and speed to turn complicated concepts into high-performing products, whether they are for large-scale production or specialist parts.
FAQs
What is the process of die casting?
Die casting is a method for making metal pieces with complicated forms. It pushes molten metal into a mold with a lot of pressure.
What kinds of die casting methods are there?
There are two basic kinds: hot-chamber and cold-chamber die casting. Each one has its own pros and cons and works best with certain materials and uses.
What materials do people usually use for die casting?
People regularly employ alloys like aluminum, zinc, and magnesium. They each have their own set of qualities that make them good for certain tasks.
What are the benefits of die casting?
It works quickly, accurately, and can make shapes that are hard to make. This makes it a suitable choice for producing several pieces.
What are the bad things of die casting?
It can be costly to start, has constraints on materials, and might have flaws. When making pieces, you should think about these things.
What does this mean for the cost of die casting?
Costs include the tools, the materials, and the time it takes. Knowing them helps make die casting more economical.
What are some common problems with die casting?
There can be problems like porosity and misruns. But, smart design and control can help avoid them.
Is die casting a process that can last?
Yes, it can. A lot of alloys can be recycled, and people are trying to use less energy and cut down on emissions.
How does die casting stack up against other ways to cast?
Die casting has its own pros and cons compared to other procedures like sand casting and investment casting. These things assist you pick the optimal method.
What kinds of finishing and surface treatments can be done on die-cast parts?
Machining and polishing are two options that can make things better. What the part needs will determine the right decision.
Die Casting FAQ
What is the main difference between die casting and sand casting?
Die casting uses a reusable metal mold (die) and high pressure, resulting in a very smooth finish, high accuracy, and fast cycle times. Sand casting uses a disposable sand mold and is better for very large parts and smaller quantities.
What is the typical tooling cost for die casting?
The initial tooling investment for a hardened steel die is significant, which is why the process is best suited for medium to high-volume production where the cost can be amortized over thousands of parts.
What kind of tolerances can be achieved with die casting?
As-cast tolerances are very good, typically within ±0.1mm. For tighter tolerances, we use secondary CNC machining on critical features.
What is "draft," and why do my parts need it?
Draft is a slight angle designed into the walls of the part that are parallel to the mold opening. It is essential to allow the part to be easily ejected from the die without damage.
What is the difference between "hot chamber" and "cold chamber" die casting?
Hot chamber machines are used for lower-melting-point alloys like zinc. Cold chamber machines are used for higher-melting-point alloys like aluminum, where the molten metal is ladled into the chamber for each shot.
Can you cast parts with threads?
Yes, external threads can often be cast directly. Internal threads are typically created in a secondary CNC tapping operation for better accuracy and strength.
